A recent study conducted by Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI) in Abu Dhabi, in collaboration with the US tech giant IBM, has unveiled the pivotal role of green
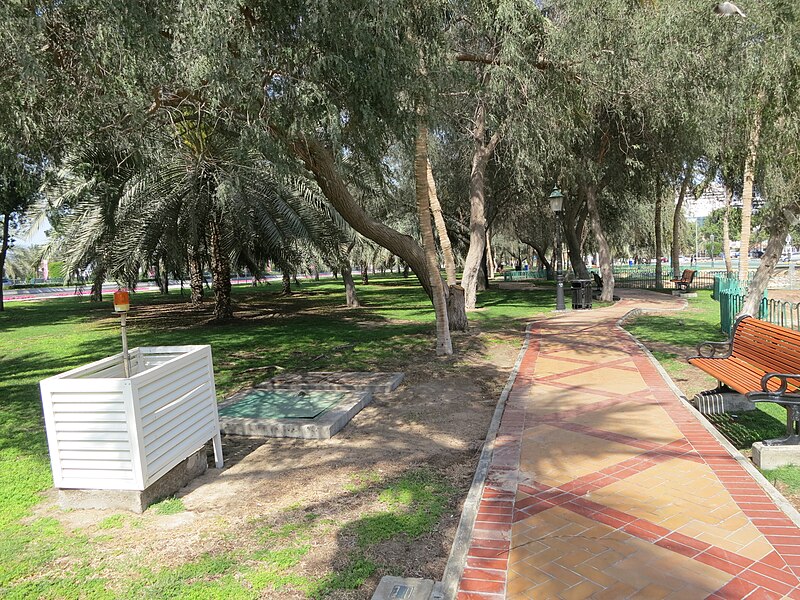
parks in Abu Dhabi in reducing urban temperatures. The study, as reported by the official agency WAM, reveals that certain areas experience a cooling effect of up to 2.2°C.
Dr. Salman Khan, Associate Professor of Computer Vision at MBZUAI, explained in an interview with the Emirates News Agency (WAM) that the study harnessed AI-enabled technology to analyze decades of satellite data. It uncovered the significant impact of vegetation and water bodies in mitigating urban "heat island" effects.
Urban heat islands occur when cities exhibit significantly higher temperatures than adjacent rural areas. This phenomenon arises due to the absorption and emission of heat by densely developed urban areas, leading to elevated local surface and air temperatures, thereby exacerbating global warming.
Part of the "AI-enabled Urban Heat Island Detection and Mitigation" project, the study aims to identify factors contributing to urban heat islands and devise strategies to alleviate them.
Dr. Khan highlighted the substantial cooling effects of specific parks. For instance, Masdar Park in Masdar city has reduced temperatures by 2.2°C in its vicinity. Similarly, Umm Al Emarat Park in Abu Dhabi City has resulted in a 1°C cooling effect in the central area of Abu Dhabi island.
These findings underscore the importance of green spaces in urban environments, which can help mitigate the adverse impacts of urban heat islands on human health and well-being.
Through the analysis of satellite data, encompassing thermal channels, vegetation, and building footprints, the study provided invaluable insights into the role of parks in reducing urban heat islands.
Dr. Khan stressed that these results can inform urban planning strategies, pinpointing areas where increased vegetation can have the most significant impact on temperature reduction. Moreover, the research showcased the potential of AI-enabled technology in forecasting the effects of urban interventions on temperature reduction.
The study's implications for urban planning and development are significant, emphasizing the imperative of prioritizing green spaces and sustainable urban design to combat the negative effects of urban heat islands.
Dr. Khan concluded by noting the success of projects in Abu Dhabi island, where the proliferation of vegetation over the past decade has substantially reduced temperatures. This underscores the potential for further enhancing vegetation in urban areas to mitigate the adverse impacts of urban heat islands. Photo by FritzDaCat, Wikimedia commons.